Hip
Anatomy
-
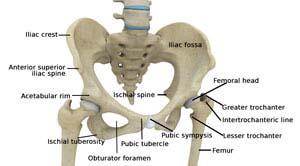
Normal Hip Anatomy
The hip joint is the largest weight-bearing joint in the human body. It is also referred to as a ball and socket joint and is surrounded by muscles, ligaments, and tendons. The thigh bone or femur and the pelvis join to form the hip joint.
-
Physical Examination of Hip
The hip joint is a ball and socket joint. The ball is the head of the femur (thighbone) that fits in the acetabulum (the hip socket). Tendons, muscles, and ligaments hold the joint in place. Articular cartilage covers the acetabulum and the femoral head. The synovial membrane of the hip joint secretes the synovial fluid which lubricates the joint enabling smooth movement.
Conditions
-
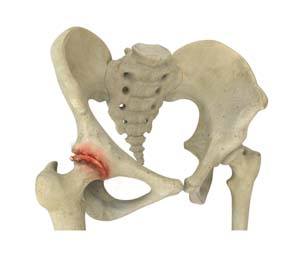
Avascular Necrosis
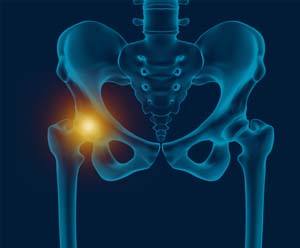
Avascular necrosis, also called osteonecrosis, is a condition in which bone death occurs because of inadequate blood supply to it. Lack of blood flow may occur when there is a fracture in the bone or a joint dislocation that may damage nearby blood vessels. Hip joint is most commonly affected; however, the knee and shoulder may also be involved.
Hip Treatments
-
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy is an exercise program that helps you to improve movement, relieve pain, encourage blood flow for faster healing, and restore your physical function and fitness level. It can be prescribed as an individual treatment program or combined with other treatments. It involves a combination of education, manual therapy, exercises and techniques such as water, heat, cold, electrical stimulation and ultrasound.
-
Patient-Specific Hip Options
The hip is a ball and socket joint which connects your thigh and hip bone. It is a crucial part of your anatomy that bears a large amount of force. Your hip may be subjected to injuries, damage, strains, inflammation, dislocation or fractures due to sports activities, overuse, falls and accidents.
-
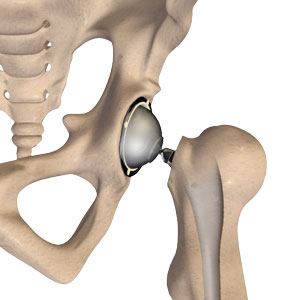
Total Hip Replacement
Total hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which the damaged cartilage and bone is removed from the hip joint and replaced with artificial components.
-
Hip Implants
Hip implants are artificial devices that form the essential parts of the hip joint during a hip replacement surgery. The hip implants vary by size, shape, and material. Various components of a hip implant may be used for a hip replacement surgery. The components used may depend on the extent of damage to the hip joint, and the preference of the orthopaedic surgeon performing the procedure.
-
Pre-op and Post-op Hip Guidelines
Planning for your hip surgery prepares you for the operation and helps to ensure a smooth surgery and easier recovery. Here are certain pre-operative and post-operative guidelines which will help you prepare for hip surgery.
-
Caregivers Guide for the Hip
When your friend or loved one has undergone a hip replacement surgery, as a caregiver, you will play an important role in his/her recovery. There are various aspects you need to be aware of to ensure the safety, comfort and recovery of the patient.
-
Hip Fracture Prevention
Healthy lifestyle choices in early adulthood help in building high bone mass and reduce risk of bone- related diseases in later years.